July 17, 2023
Study Underscores Significant Implications for Cancer and Obstetrics Medicine, as well as Diagnostics, and Preventative Therapy
A team of researchers from the University of Maryland School of Maryland’s (UMSOM) Institute of Human Virology (IHV), a Center of Excellence of the Global Virus Network (GVN), published new findings that emphasize the crucial role of the urinary and genital tract microbiota in adverse pregnancy outcomes and genomic instability that originate in the womb during fetal development.
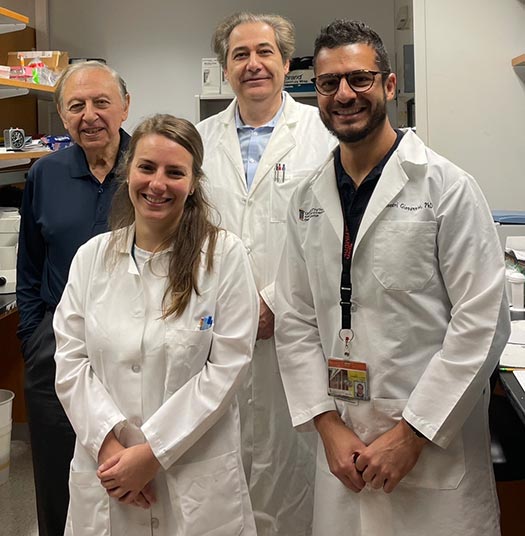 The study, published on July 17 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), established a new link between genomic instability, reduced fertility, and a protein from Mycoplasma fermentans, a kind of bacterium that commonly colonizes the urogenital tract in humans.
The study, published on July 17 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), established a new link between genomic instability, reduced fertility, and a protein from Mycoplasma fermentans, a kind of bacterium that commonly colonizes the urogenital tract in humans.
This research was spearheaded by Davide Zella, PhD, Assistant Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at UMSOM’s IHV and Robert Gallo, MD, The Homer & Martha Gudelsky Distinguished Professor in Medicine, Co-Founder and Emeritus Director of UMSOM’s IHV, and Co-Founder and Chair of the Scientific Leadership Board of the Global Virus Network.
"Our results not only broaden our understanding of the interplay between the urogenital tract microbiota and human reproductive health, but also shed light on the previously unidentified contribution of the human microbiota to genetic abnormalities," said co-lead author on the study Francesca Benedetti, PhD, Research Associate of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology in UMSOM’s IHV.
“We aim to further explore the mechanisms underlying these findings and their potential implications for preventing and treating chromosomal abnormalities and genetic diseases,” said co-lead author Giovannino Silvestri, PhD, former Research Associate of Medicine in UMSOM’s IHV.
The human microbiota is known to affect metabolism, susceptibility to infectious diseases, immune system regulation, and more. One of these bacterial components, Mycoplasmas, have been linked to various cancers.
The research team has been studying one Mycoplasma protein, DnaK, which belongs to a family of proteins that safeguards other bacterial proteins against damage and aids in their folding when they are newly made, acting as a so-called ‘chaperone.’ However, while this protein is advantageous for bacteria, its effects on animal cells are less favorable. To this regard, the team had previously demonstrated that this DnaK is taken up by the body’s cells and it interferes with key proteins involved in preserving DNA integrity and in cancer prevention, such as the tumor suppressor protein p53.
For this latest study, researchers created mice that make the DnaK protein normally produced by the bacterium Mycoplasma fermentans. These mice with exposure to DnaK accrued genomic instability in which entire sections of the genome were duplicated or deleted, resulting in mice with varying numbers of copies of certain genes.
The team noticed that some of these mice from 3-5 weeks of age had problems with movement and coordination. They found that these mice have a deletion in the Grid2 gene, which in humans leads to the rare genetic disease known as spinocerebellar ataxia-18 (SCAR18) that causes delayed development of skilled movements and intellectual disabilities.
“Remarkably, this instance marks the first time a mouse model successfully recapitulated a human genetic disease de novo, showcasing this model's potential for further cancer biology research,” said Dr. Zella.
More than a third of the female mice that made the DnaK protein were unable to get pregnant. Additionally, more than 20 percent of the pups born from moms with the DnaK protein had some sort of birth defect/deformity.
 “The occurrences of genomic instability, in the form of increased number of copy number variations, could explain the decreased fertility and the increased instances of abnormally developed fetuses we observed upon DnaK exposure,” said Dr. Gallo. “These data build upon our initial work which discovered the disruptive role of DnaK on key proteins involved in the proper repair of damaged DNA, which are also known to play a role in the onset of copy number variations. Our ongoing commitment is to better understand the potential implications of these findings in cellular transformation and cancer.”
“The occurrences of genomic instability, in the form of increased number of copy number variations, could explain the decreased fertility and the increased instances of abnormally developed fetuses we observed upon DnaK exposure,” said Dr. Gallo. “These data build upon our initial work which discovered the disruptive role of DnaK on key proteins involved in the proper repair of damaged DNA, which are also known to play a role in the onset of copy number variations. Our ongoing commitment is to better understand the potential implications of these findings in cellular transformation and cancer.”
UMSOM Dean Mark T. Gladwin, MD, who is also Vice President for Medical Affairs, University of Maryland, Baltimore and the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor, commended the work. “The researchers raise a significant question regarding whether DnaK can interfere with fetal development in humans. An important next step would be to investigate whether neutralizing either the bacteria or this protein could preserve fertility and prevent certain birth defects,” he said.
About the Institute of Human Virology
Formed in 1996 as a partnership between the State of Maryland, the City of Baltimore, the University System of Maryland, and the University of Maryland Medical System, the IHV is an institute of the University of Maryland School of Medicine and is home to some of the most globally-recognized and world-renowned experts in all of virology. The IHV combines the disciplines of basic research, epidemiology, and clinical research in a concerted effort to speed the discovery of diagnostics and therapeutics for a wide variety of chronic and deadly viral and immune disorders, most notably HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. For more information, visit ihv.org and follow us on Twitter @IHVmaryland.
About the University of Maryland School of Medicine
Now in its third century, the University of Maryland School of Medicine was chartered in 1807 as the first public medical school in the United States. It continues today as one of the fastest growing, top-tier biomedical research enterprises in the world -- with 46 academic departments, centers, institutes, and programs, and a faculty of more than 3,000 physicians, scientists, and allied health professionals, including members of the National Academy of Medicine and the National Academy of Sciences, and a distinguished two-time winner of the Albert E. Lasker Award in Medical Research. With an operating budget of more than $1.2 billion, the School of Medicine works closely in partnership with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System to provide research-intensive, academic and clinically based care for nearly 2 million patients each year. The School of Medicine has nearly $600 million in extramural funding, with most of its academic departments highly ranked among all medical schools in the nation in research funding. As one of the seven professional schools that make up the University of Maryland, Baltimore campus, the School of Medicine has a total population of nearly 9,000 faculty and staff, including 2,500 students, trainees, residents, and fellows. The combined School of Medicine and Medical System ("University of Maryland Medicine") has an annual budget of over $6 billion and an economic impact of nearly $20 billion on the state and local community. The School of Medicine, which ranks as the 8th highest among public medical schools in research productivity (according to the Association of American Medical Colleges profile) is an innovator in translational medicine, with 606 active patents and 52 start-up companies. In the latest U.S. News & World Report ranking of the Best Medical Schools, published in 2021, the UM School of Medicine is ranked #9 among the 92 public medical schools in the U.S., and in the top 15 percent (#27) of all 192 public and private U.S. medical schools. The School of Medicine works locally, nationally, and globally, with research and treatment facilities in 36 countries around the world. Visit medschool.umaryland.edu.
Contact
Institute of Human Virology
Nora Samaranayake
Chief Communications & Public Affairs Officer
(443) 823-0613 (phone)
(410) 706-1952 (fax)
nsamaranayake@ihv.umaryland.edu
Related stories

Friday, April 02, 2021
Baltimore Sun: Q&A with Dr. Robert Gallo: ‘The world has to be linked to fight a pandemic’
Robert Gallo, the eminent virologist best known as co-discoverer of the AIDS virus, says the world needs a system to confront viral disease that’s free of politics and primed to quickly warn nations about new threats as if “the bad Martians are coming.” The uneven and politicized response to the coronavirus pandemic, with a worldwide toll approaching 3 million, including 553,000 deaths in the United States, proves Gallo’s point.

Thursday, February 18, 2021
The Science Advisory Board: The next generation of COVID-19 vaccines: Gallo on next steps
With emergency authorizations for several COVID-19 vaccines under our belt, the question remains if these vaccines will be enough to carry us through the end of the pandemic. Experts agree that there will likely need to be additional vaccines to achieve full recovery. In this two-part series, we discuss what a next-generation COVID-19 vaccine might look like, and which candidates are in the running for authorizations.

Friday, February 12, 2021
The Washington Post: Scientists said claims about China creating the coronavirus were misleading. They went viral anyway.
The spread of the unverified assertions by Chinese scholar Li-Meng Yan, widely dismissed as “flawed,” show how vulnerable scientific sites are to misuse and misunderstanding.

Friday, February 12, 2021
China CDC Weekly: Commentary by Dr. Robert C. Gallo
The Great Coronavirus Pandemic of 2019−2021: the Future and the Requirement for China-America Cooperation - Over the past century, the great pandemics and most epidemics (defined as virus presence and disease induction presenting more than the expected number of infections in a population) were caused by the sudden outbreak of an RNA virus such as the pandemics of influenza, polio, and HIV/AIDS and the epidemics of influenza, Ebola, Dengue, Zika, West Nile, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), and Chikungunya.

Friday, December 11, 2020
Bloomberg TV Asia: Dr. Robert Gallo on COVID-19 Vaccines
Dr. Robert Gallo, co-founder and international scientific advisor of the Global Virus Network and the co-founder and director of the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, discusses the rollout of the Covid-19 vaccines. The first Covid-19 vaccine expected to be deployed in the U.S. won the backing of a panel of government advisers, a step that will likely help clear the way for emergency authorization by the Food and Drug Administration. Gallo, who co-discovered HIV as the cause of AIDS in 1984, speaks with Haidi Stroud-Watts and Shery Ahn on "Bloomberg Daybreak: Australia." (Source: Bloomberg)
Wednesday, November 11, 2020
Dr. Robert Gallo on Bloomberg Asia on COVID Vaccine Prospects
Dr. Robert C. Gallo, The Homer & Martha Gudelsky Distinguished Professor in Medicine, co-founder and director of the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and co-founder and international scientific advisor of the Global Virus Network, discusses the timeline and safety of Covid-19 vaccine trials. He speaks with Shery Ahn and Haidi Stroud-Watts on "Bloomberg Daybreak: Asia".
Sunday, November 01, 2020
The Scientist: How Some Vaccines Protect Against More than Their Targets
As researchers test existing vaccines for nonspecific protection against COVID-19, immunologists are working to understand how some inoculations protect against pathogens they weren’t designed to fend off.

Friday, August 28, 2020
WYPR: Could Polio Vaccine Corral Covid-19?
A safe, effective vaccine against Covid-19 could resurrect jobs, send kids back to classrooms--change our lives. But how safe and effective? And how quickly can we have it? Dr. Robert Gallo, the AIDS-research pioneer now leading virus science at the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and the Global Virus Network, argues we could get much of the benefit by inoculating people with an old, very cheap drug -- the oral Polio vaccine developed seven decades ago. Gallo contends it would trigger our ‘innate immunity’-- the body’s emergency response when a threat shows up.

Monday, August 03, 2020
Eureka, Charles River Laboratories: Could the Oral Polio Vaccine be Used to Prevent COVID-19?
Virologist Robert Gallo, MD, has had a long and storied career in academic and government research. He is the Homer & Martha Gudelsky Distinguished Professor in Medicine, co-founder and director of the Institute Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and co-founder and international scientific adviser of the Global Virus Network. Despite his deep roots in HIV, Dr. Gallo’s current focus is, not surprisingly, COVID-19, which emerged in China last year and within four months morphed into a full-blown pandemic. As usual, Dr. Gallo’s research strategy has raised eyebrows. Unlike the antibody and RNA vaccines that are all the rage in COVID-19 science, Gallo is putting his energies behind repurposing the oral polio virus vaccine developed in the 1950s by Albert Sabin.
Friday, July 31, 2020
RollingStone-Useful Idiots: Dr. Robert Gallo on a COVID-19 Vaccine
Dr. Robert Gallo, director of the Institute for Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, joins the show to give his take on the prospects for an effective COVID-19 vaccine. Gallo is skeptical of the approach many organizations are taking with antibody vaccines, citing the similarly low efficacy those treatments had with HIV due to the low durability of the antibodies. Dr. Gallo’s research is mainly related to Oral Polio Vaccine, which he thinks needs to be tested more in regard to innate immunity.

Friday, July 24, 2020
A Statement from the Leadership of the Institute of Human Virology and the Global Virus Network on the Passing of Renowned Chinese Virologist Yi Zeng
The IHV at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and the Global Virus Network (GVN), a coalition comprised of the world’s preeminent human and animal virologists from 55 Centers of Excellence and 10 Affiliates in 32 countries, collectively mourns the passing of Professor Yi Zeng, MD, Academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, former President of the Chinese Academy of the Preventive Medicine and former Dean of the College of Life Science and Bioengineering at Beijing University of Technology.

Monday, July 20, 2020
NPR: Early Oxford-AstraZeneca Coronavirus Vaccine Data 'Encouraging,' Scientists Say
Dr. Robert Gallo is quoted about an experimental vaccine candidate being developed by AstraZeneca and Oxford University to protect against COVID-19 that triggered an immune response against the coronavirus and appeared to be safe.
Tuesday, July 07, 2020
Courthouse News Service: Global Progress on Ending HIV/AIDS Derailed by Covid-19
A United Nations program aimed at eliminating HIV/AIDS released a report Monday showing that the global response to the epidemic has fallen far short of goals set for 2020, in large part due to the coronavirus pandemic.

Monday, July 06, 2020
Sputnik Radio: What If There Is No Vaccine for COVID-19?
On today's episode of Loud & Clear, Brian Becker and John Kiriakou are joined by Robert Gallo, MD, the Homer & Martha Gudelsky Distinguished Professor in Medicine, co-founder and director of the Institute Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and co-founder and international scientific adviser of the Global Virus Network. What would you think if someone told you that we already have a vaccine that at least helps fight Covid-19? That may already be the case. Two American scientists, Dr. Robert Gallo and Dr. Konstantin Chumakov, are positing that decades-old live vaccines for things like polio and tuberculosis strengthen the immune system’s first line of defense a more general way to fight infection. And the history books show us that that sometimes translates into at least some cross-protection against completely different viruses.

Friday, July 03, 2020
KUSI San Diego News: Dr. Robert Gallo suggests an oral polio vaccine could help fight coronavirus
Dr. Robert Gallo from the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and Global Virus Network wrote an op-ed in the Wall Street Journal earlier this week. The opinion piece stated that OPV, oral polio vaccine, could be a cheap and effective way to fight coronavirus. Dr. Gallo discussed his opinion piece on Good Morning San Diego.
Thursday, July 02, 2020
13D Global Strategy & Research Report
COVID-19 outbreaks are multiplying and immunity may be short-lived. Could existing “live” vaccines, which stimulate innate immunity, outshine vaccines targeting the “spike” protein?
Thursday, June 25, 2020
The New York Times: Dr. Robert Gallo: The Case for a Stopgap Vaccine
In a letter to the editor to The New York Times entitled, "Dr. Robert Gallo: The Case for a Stopgap Vaccine," the noted virologist and head of the IHV says a polio vaccine may be an ideal solution until we find a Covid-specific vaccine.
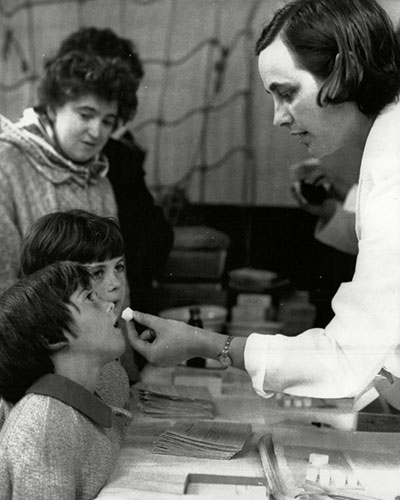

Wednesday, June 24, 2020
The New York Times: Decades-Old Soviet Studies Hint at Coronavirus Strategy
The New York Times: Decades-Old Soviet Studies Hint at Coronavirus Strategy: A married pair of virologists in Moscow tested a vaccine on their own children in the 1950s. Now, a side effect they found is sparking new hope for a defense against the coronavirus.
Friday, June 12, 2020
Institute of Human Virology and Italian Researchers Find Higher Daily Temperatures Lead to a Decrease in COVID-19 Related Deaths
Insights into population density and daily temperatures provide a path to public health strategies. The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, a Global Virus Network (GVN) Center of Excellence, in collaboration with scientists from Campus Biomedico in Rome and Ulisse Biomed and University of Trieste, in Trieste, Italy announced today the results of studies showing an inverse correlation between average high daily temperatures and COVID-19 related death rates in different geographical areas.

Friday, June 12, 2020
The Washington Post: We shouldn’t care who wins the vaccine ‘race’
Dr. Robert Gallo writes a Letter to the Editor to The Washington Post entitled, “We shouldn’t care who wins the vaccine ‘race’,” regarding their June 4 front-page article “Cold War echoes in race for vaccine,” about the “race” among nations, notably the United States, China, and Russia and other European nations for development of a vaccine against the novel coronavirus.

Friday, June 12, 2020
CNN Health: An Existing Polio Vaccine Could Help Protect Against Coronavirus, Top Experts Say
CNN: There is plenty of evidence that existing inoculations such as polio vaccines protect children against a wide range of infections and it's worth trying them out against the new coronavirus, a team of experts wrote in Science magazine Thursday.

Thursday, June 11, 2020
NBC News: Polio Vaccine Could Give Temporary Protection Against COVID-19, Scientists Hope
NBC News: As the world waits for a coronavirus vaccine, some scientists are proposing that existing vaccines could give the body’s immune system a much-needed temporary boost to stave off infection. It’s still unclear whether such an approach would work, and some experts are skeptical. Others — including researchers in Israel, the Netherlands and Australia — are already investigating whether a tuberculosis vaccine could help jump-start the immune system and make COVID-19 less deadly, though the World Health Organization strongly advises against using that vaccine until it’s proven effective against the coronavirus.
Monday, May 11, 2020
BBC Global News Interviews Dr. Robert Gallo on Oral Polio Vaccine for SARS-CoV-2 and More
Dr. Robert Gallo appeared on BBC World News with Matthew Amroliwala for a one-on-one, lengthy interview during their Coronavirus Explained segment.
Saturday, May 09, 2020
Dr. Robert Gallo Discuss COVID-19 Research on Aljazeera News
Aljazeera discusses the status of therapy, testing and vaccine research on SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 with Dr. Robert Gallo.

Thursday, May 07, 2020
The Disappointing Truth About Antibody Testing: There’s still a lot we don’t know about COVID-19
Dr. Robert Gallo discusses the status of COVID-19 antibody test with Vox's The Verge
Wednesday, May 06, 2020
The Coronavirus Appears to have Mutated. What Does that Mean for Contagiousness?
While small mutations in the virus's genetic code are evident, it's unclear what these changes mean for people, if anything at all.

Saturday, May 02, 2020
IHV's Dr. Robert Gallo on FOX's Full Court Press with Greta Van Susteren
Overtime: Dr. Robert Gallo talks coronavirus treatments and antibody testing.

Saturday, May 02, 2020
Dr. Robert Gallo on iHeart Radio to Discuss COVID-19
Ryan Gorman hosts an iHeartRadio nationwide special featuring experts on COVID-19-related issues, including the co-founder and director of the Institute Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, the senior vice president for U.S. Programs & Advocacy at Save the Children, and the managing editor of the Military Times. Topics range from a discussion about why some people infected by the coronavirus are asymptomatic, while others face severe reactions and even death, to assistance for impoverished children, and a breakdown of the impact the virus is having on the U.S. military and veterans.

Friday, May 01, 2020
Could an Oral Polio Vaccine Stop the Coronavirus Pandemic?
A YouTube video by the American Chemical Society and produced by PBS.

Tuesday, December 04, 2018
Institute of Human Virology Researchers Discover That a Bacterial Protein Promotes Cancer
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) announced today the discovery that DnaK, a protein of the bacterium mycoplasma, interferes with the mycoplasma-infected cell’s ability to respond to and repair DNA damage, a known origin of cancer.

Monday, December 03, 2018
Institute of Human Virology Names Dr. Man Charurat as Director of the Center for International Health, Education, and Biosecurity
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine today announced the appointment of Man E. Charurat, PhD, MHS, Professor of Medicine and Director of the Division of Epidemiology and Prevention at the IHV as the Director of IHV’s Center for International Health, Education, and Biosecurity (CIHEB). Dr. Charurat will replace Deus Bazira, DrPH, MPH, MBA. The announcement was made by Robert C. Gallo, MD, The Homer & Martha Gudelsky Distinguished Professor in Medicine, Co-Founder and Director of the IHV, and Co-Founder and Director of the Global Virus Network (GVN).

Wednesday, September 19, 2018
Institute of Human Virology (IHV) Awarded $12M to Combat Opioid Epidemic Through Clinical Research Trials
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine will lead a $12 million dollar project to improve the morbidity and mortality of people with opioid use disorder (OUD). Utilizing a novel compound, IHV researches will implement a series of investigations, entitled SEARCH, to evaluate the underlying mechanisms of craving reduction as a strategy to prevent opioid misuse, dependence, and relapse. The grant is awarded through the National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) Helping to End Addiction Long-term (HEAL) Initiative, made possible through groundbreaking funding from the U.S. Congress.

Tuesday, December 12, 2017
A Statement from the Leadership of the Institute of Human Virology on the Passing of Stewart Greenebaum
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine mourns the passing of Stewart Greenebaum, a lifelong Baltimore resident, former president of Greenebaum and Rose Associates, and past chairman of the IHV Board of Advisors, as well as a guiding force in the establishment of the IHV at the University of Maryland, Baltimore.

Wednesday, November 29, 2017
To Mark World AIDS Day, Institute of Human Virology Releases Video on Dr. Robert Gallo
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) released a video on Dr. Robert Gallo, a trailblazer in HIV research, in advance of World AIDS Day, December 1. While many know Dr. Gallo for his pioneering work in AIDS research, the short video focuses on Dr. Gallo’s life and legacy in its entirety, including his pioneering discovery of human retroviruses.

Tuesday, October 25, 2016
"A Call to End HIV/AIDS in America" IHV Director Dr. Robert Gallo's Op-Ed in the Huffington Post
As the new Administration is presented with great challenges facing the United States, one will be a longtime foe, the U.S. HIV/AIDS epidemic. Since President Barack Obama was elected in 2008, I have publicly called on our country’s leaders to utilize the largest global health initiative in history - the President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) - as a model to address the U.S. epidemic.

Monday, August 22, 2016
Institute of Human Virology (IHV) Awarded $14.4M for HIV Vaccine Research
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) announced a $14.4M grant from NIAID to advance HIV vaccine research to solve a major challenge: produce long-lasting antibodies to protect against HIV infection.

Thursday, March 10, 2016
UM SOM Establishes Two Endowed Professorships Through Private Gifts and Matching State Funds
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UM SOM) Dean E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, announced today that the School has been awarded matching funds from the Maryland Department of Business and Economic Development (DBED) as part of the Maryland E-Nnovation Initiative Fund program. The funds, when combined with private philanthropy, will enable UM SOM to establish two new endowed professorships – one in human virology and vaccine development, the other in surgical science and entrepreneurship.

Tuesday, September 29, 2015
Institute of Human Virology Hosts International Meeting of Prominent AIDS Researchers
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine is hosting IHV’s 17th Annual International Meeting Sunday, September 27 through Wednesday, September 30 at the Baltimore Marriott Waterfront Hotel in Baltimore, Maryland.